How Does The Calendar Put Spread Work in Options Trading?
Calendar Put Spread - Introduction
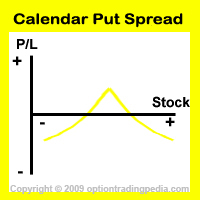
The Calendar Put Spread, being one of the three popular forms of Calendar Spreads (the other 2 being the Calendar Call Spread and Ratio Calendar Spread), is a neutral options strategy that profits when the underlying asset stays stagnant or goes down slightly.
Unlike the Calendar Call Spread, Calendar Put Spreads uses put options instead of call options.
A Calendar Put Spread profits primarily from the difference in rate of premium decay between the near term short options and the long term LEAPs.
This is possible because near term option premiums decay faster than long term option premiums.
|
|
Because you need to buy LEAPs which are more expensive than the short term options that you will write, this strategy results in a net debit and is therefore a form of Debit Spread.
(These classifications are only for a deeper understanding of the kinds of option spread strategies and is not necessary for the execution of these strategies.)
When To Use Calendar Put Spread?
One should use a Calendar Put Spread when one wishes to profit from an underlying asset that is expected to stay stagnant or within a tight price range while keeping a long term put options position for when the stock breaks out to downside in future.
How To Use Calendar Put Spread?
Diagonal Calendar Put Spread
In this version of the Calendar Put Spread, all you have to do is to purchase an In the Money (ITM) LEAPS and then sell At the Money (ATM) or Out of the Money (OTM) near term Puts against the LEAP.
|
Example : Assuming QQQQ trading at $45 now. Buy To Open 10 contracts of QQQQ Jan 2008 $46 Put options at $5.70. Sell To Open 10 contracts of QQQQ Jan 2007 $45 Put at $0.75. |
Read the full tutorial on Diagonal Calendar Put Spread.
In this version of the Calendar Put Spread, you will purchase At The Money (ATM) LEAP Put options and then sell ATM near term Puts against the LEAP Put options.
|
Example : Assuming QQQQ trading at $45 now. Buy To Open 10 contracts of QQQQ Jan 2008 $45 Put options at $4.70. Sell To Open 10 contracts of QQQQ Jan 2007 $45 Put at $0.75. |
Read the full tutorial on Horizontal Calendar Put Spread.
Trading Level Required For Calendar Put Spread
A Level 3 options trading account that allows the execution of debit spreads is needed for the Calendar Put Spread. Read more about Options Account Trading Levels.
Profit Potential of Calendar Put Spread :
Both the Diagonal Calendar Put Spread and the Horizontal Calendar Put Spread makes their maximum profit when the underlying stock closes at the strike price of the short put options during expiration of the short put options.
Profit Calculation of Calendar Put Spread:
The value of a Put Time Spread during expiration of the short put options can only be arrived at using an options pricing model such as the Black-Scholes Model because the expiration value of the long term put options can only be arrived at using such a model.
Risk / Reward of Calendar Put Spread:
Upside Maximum Profit: Limited
Maximum Loss: Limited
(limited to net debit paid)
Break Even Point of Calendar Put Spread:
The breakeven point of a Calendar Put Spread is the point below which the position will start to lose money if the underlying asset rises or falls strongly and can only be calculated using the Black-Scholes model.
Advantages Of Calendar Put Spread:
Disadvantages Of Calendar Put Spread:
Adjustments for Calendar Put Spreads Before Expiration :
1. If you wish to profit from a drop in the underlying asset, you could buy back the short Put options before it expires and allow the LEAP Put Options to continue its profit run.

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
| Javascript Tree Menu |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by