|
|
Vertical Spreads - Introduction
Almost all options strategies are made up of what are known as spreads.
Options Spreads are simply simultaneously buying and shorting different
options of the same type on the same underlying stock. For example, Buying a $30 strike Call Option and simultaneously shorting its $33 strike
call option is a spread. Spreads are extremely important in options trading because spreads enable different risk/reward profiles to be created,
giving options trading its legendary versatility. There are many types of spreads namely; Horizontal Spreads, Diagonal Spreads, Ratio Spreads
and Vertical Spreads.
This tutorial shall explain what Vertical Spreads are and explore the different types of Vertical Spreads.
Vertical Spreads - Content
What are Vertical Spreads |
Types of Vertical Spreads |
Purpose of Vertical Spreads |
Advantages and Disadvantages
|
What are Vertical Spreads?
Vertical Spreads are options spreads made up of options of the same underlying, same type, same expiration month but different strike prices.
Vertical Spreads are named Vertical Spreads because the options that are involved in a vertical spread are stacked up vertically on an options
chain.
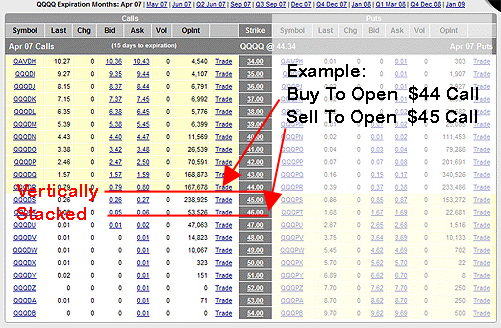
The example in the picture above is a Bull Call Spread on the QQQQ buying its April $44 strike call options and shorting its April $45 call options.
Yes, Bull Call Spreads are Vertical Spreads as well.
 Vertical spread is simply a way of classifying options strategies using options of the same type and month but different strikes. Knowing or not knowing such classification does not actually affect your options trading in anyway. Vertical spread is simply a way of classifying options strategies using options of the same type and month but different strikes. Knowing or not knowing such classification does not actually affect your options trading in anyway.
|
Types of Vertical Spreads
There are 2 main types of Vertical Spreads; Bull Vertical Spread and Bear Vertical Spread.
Bull Vertical Spreads are Vertical Spreads with a bullish outlook. There are two main bull vertical spread strategies;
Bull Call Spread
and Bull Put Spread.
Bear Vertical Spreads are vertical spreads with a bearish outlook. There are two main bearish vertical spread strategies;
Bear Call Spread
and Bear put Spread.
Vertical Spreads can also be either a debit spread or a
credit spread.
Bull Call Spread and Bear Put Spread are debit Vertical Spreads because you need to pay money to put on these spreads
while Bull Put Spread and Bear Call Spreads are credit Vertical Spreads because you receive money for putting on these spreads.
STOCK PICK MASTER!
"Probably The Most Accurate Stock Picks In The World..."
Purpose of Vertical Spreads
The purposes of Vertical Spreads are in reducing the upfront payment on call or put options purchase or reducing the
margin requirement when
shorting call or put options. Options traders need to take note that spreads involve higher commissions due to the need to put on additional
legs to a single options trading position, that is why options traders should use Vertical Spreads only when the cost saving overcomes the higher commission cost.
In a Bull Call Spread, which is a debit bullish vertical spread, selling the
out of the money call options serves to reduce the
cost of buying the nearer the money call options.
Bull Call Spread Example :
Assuming the QQQQ Jan44Calls are asking for $1.50 while the QQQQ Jan46Calls are bidding for $0.20.
By shorting / writing the QQQQ Jan46Calls, the position now cost only $1.50 - $0.20 = $1.30, instead of the full $1.50 if you only
bought the Jan44Calls outright. This is especially useful if QQQQ is not expected to exceed $46 in price.
|
In a Bear Put Spread, which is a debit bearish vertical spread, selling the out of the money put options serves to reduce the cost of buying the
nearer the money put options.
Bear Put Spread Example :
Assuming the QQQQ Jan44Puts are asking for $1.50 while the QQQQ Jan42Puts are bidding for $0.20.
By shorting / writing the QQQQ Jan42Puts, the position now cost only $1.50 - $0.20 = $1.30, instead of the full $1.50 if you only
bought the Jan44Puts outright. This is especially useful if QQQQ is not expected to go lower than $42 in price.
|
In a Bull Put Spread, which is a credit bullish vertical spread, buying the out of the money put options serves to reduce the margin required
when shorting the nearer the money put options.
Bull Put Spread Example :
Assuming the QQQQ Jan44Puts are bidding for $1.30 while the QQQQ Jan42Puts are asking for $0.30.
By buying the QQQQ Jan42Puts, the position requires much lesser margin than when Selling To Open the Jan44Puts itself. However, that also
reduces the maximum profit from $1.30 to $1.30 - $0.30 = $1.00
|
In a Bear Call Spread, which is a credit bearish vertical spread, buying the out of the money call options serves to reduce the margin required
when shorting the nearer the money call options.
Bear Call Spread Example :
Assuming the QQQQ Jan44Calls are bidding for $1.30 while the QQQQ Jan46Calls are asking for $0.30.
By buying the QQQQ Jan46Calls, the position requires much lesser margin than when Selling To Open the Jan44Calls itself. However, that also
reduces the maximum profit from $1.30 to $1.30 - $0.30 = $1.00
|
Advantages of Vertical Spreads
Cost saving when putting on debit options trading positions.
Lower margin when putting on credit options trading positions.
Higher ROI on the same move due to lower cost for debit options trading positions.
Disadvantages of Vertical Spreads
Higher commissions due to additional trades.
Lower maximum profit when putting on credit options trading positions.
Changes maximum profit potential of debit options trading positions from unlimited to limited.
Needs position to be held to expiration for the offsetting leg to serve its purpose in a debit options trading position.
|