How Does Bear Call Spread Work in Options Trading?
Bear Call Spread - Introduction
A Bear Call Spread is a bearish option strategy that works in the same way a Bear
Put Spread does, profiting when the underlying stock drops.
The Bear Call Spread is simply a naked call write
which minimizes margin requirement
and limits potential loss by purchasing a higher strike price call option.
|
|
Bear Call Spread - Classification
Strategy : Bearish | Outlook : Moderately Bearish | Spread : Vertical Spread | Debit or Credit : Credit
When To Use Bear Call Spread?
One should use a Bear Call Spread when one is moderately confident of a drop in the underlying asset and wants some protection and profit should the underlying asset remains stagnant .
How To Use Bear Call Spread?
Establishing a Bear Call Spread involves the purchase of an At The Money or Out of The Money call option on the underlying asset while simultaneously writing (sell to open) an In the Money or At The Money call option on the same underlying asset with the same expiration month .
Bear Call Spread ExampleAssuming QQQQ at $44. Buy To Open 10 QQQQ Jan44Call, Sell To Open 10 QQQQ Jan43Call If you expect QQQQ to go down beyond $42 by expiration, you will Sell to Open QQQQ Jan42Call instead. |
Which strike prices to choose also depends on your desired effect. If the Bear Call Spread is established by selling ATM call option and buying OTM call options, the position needs only stay stagnant or drop to result in a profit, hence a higher profit probability. The drawback is that this method decreases the maximum profit potential of the Bear Call Spread. Again, like all option trading strategies, there is a trade-off between maximum profit and profit probability.
Bear Call Spread ExampleAssuming QQQQ at $44. Buy To Open 10 QQQQ Jan45Call, Sell To Open 10 QQQQ Jan44Call |
The profitability of a bear call spread can be enhanced or better guaranteed by legging into the position properly. A bear call spread can also be transformed into a Deep ITM Bear Call Spread for better reward risk ratio and possibly even an arbitrage.
Trading Level Required For Bear Call Spread
A Level 4 options trading account that allows the execution of credit spreads is needed for the Bear Call Spread. Read more about Options Account Trading Levels.
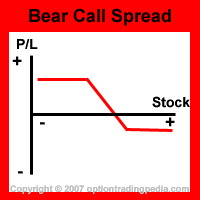
Profit Potential of Bear Call Spread :
Bear Call Spreads profits in 2 ways. Firstly, if the stock goes down, the short call option goes down in price and eventually expire out of the money when
the underlying asset drops beyond the strike price of the short call option (example 1 above).
Secondly, while the underlying asset stays stagnant, the premium on the more expensive short call
option will continue to decay until it has no value thereby allowing one to pocket the price of the short option (example 2 above).
Being a credit spread, the maximum profit potential of a Bear Call Spread is the net credit gained when the position is put on.
This occurs when the short call option expires out of the money.
Profit Calculation of Bear Call Spread:
Maximum Return = Net Credit
Bear Call Spread ExampleBuy to open 10 QQQQ Jan44Call for $1.05 per contract and sell to open 10 QQQQ Jan43call for $1.85 per contract Max. Risk = Difference in Strike - Net Credit = ($44 - $43) - $0.80 = $0.20 when QQQQ close above $44 Following up from the above example: Buy to open 10 QQQQ Jan45Call for $0.60 per contract and sell to open 10 QQQQ Jan44Call for $1.05 per contract Max. Return = $1.05 - $0.60 = $0.45 when QQQQ close below $44 Max. Risk = Difference in strike - net credit = ($45 - $44) - $0.45 = $0.55 when QQQQ close above $45 Break Even = Lower Strike + Net credit = $44 + $0.45 = $44.45 |
Notice that using higher strike prices for a Bear Call Spread results in a lower maximum profit but a much more favorable profit probability and a maximum loss that occurs at a much higher point.
Risk / Reward of Bear Call Spread
Upside Maximum Profit: Limited
Maximum Loss: Limited
Break Even Point of Bear Call Spread
BEP: Lower Strike + Net credit
Advantages Of Bear Call Spread
:: Loss is limited if the underlying financial instrument rises instead of falls.
:: If the underlying instrument fails to drop beyond the strike price of the out of the money short call option, the profit yield will be
greater than just buying put options.
:: Able to profit even when the underlying asset remains completely stagnant.
:: Lower risk than simply writing naked call options as maximum downside is limited by the long ATM/OTM call option.
Disadvantages Of Bear Call Spread
:: There will be more commissions involved than simply buying put options or just selling naked call options.
:: There will be no more profits possible if the underlying asset drops beyond the strike price of the short call option.
:: Because it is a credit spread, there is a margin requirement in order to put on the position.
:: As long as the short call options remain in the money, there is a possibility of it being assigned. You may then have
to purchase the underlying stock to meet the short call obligation.
Adjustments for Bear Call Spread Before Expiration
1. If your moderately bearish opinion on the underlying asset turns out to be wrong and the underlying asset continues to drop strongly
beyond the strike price of the short call option,
one could sell the out of the money long call option in order to preserve some equity from the long call option and allow the short call options to expire.
Doing so will transform the position
to a naked call write position with unlimited upside risk. One could also close out the position after the underlying asset exceeds the strike price of
the short call option and then switch to an option strategy with unlimited profit potential, like a long put buy or a long straddle.
2. If the underlying stock is determined to have the potential of turning bullish and rally significantly, you could transform the Bear Call Spread into a Short Call Ladder Spread by buying as many further out of the money call options as you have short call options. This transformation can be automatically performed without monitoring using a Contingent Order.

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
| Javascript Tree Menu |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by