What is the Deep ITM Covered Call and how is it different from a regular Covered Call?
Deep In The Money Covered Call - Definition
An options trading strategy designed to profit when a stock remains stagnant, moves up or moves down to a certain limit by purchasing the stock and writing deep in the money call options against it.
Deep In The Money Covered Call - Introduction
Unlike its more popular cousin, the Covered Call, which is a bullish options strategy that makes its maximum profit when the stock moves upwards, the Deep In The Money Covered Call is a neutral / volatile options strategy which makes its maximum profit even when the stock remains stagnant or moves up / down. Yes, profiting in all 3 directions. Due to its deep protection, its returns are also very small and if the underlying stock go all the way down like shares of Lehman Brothers did, you also stand to lose the whole position.
|
|
Differences Between Deep In The Money Covered Call and Covered Call
The most obvious difference between the Deep In The Money Covered Call (Deep ITM Covered Call) and the regular covered call is the fact that out of the money call options are written in a regular covered call and deep in the money call options are written in Deep In The Money Covered Calls.
This is the difference that made all the difference.
In a Deep In The Money Covered Call, deep in the money call options are written, which means that these call options literally offsets any price movement of the underlying stock, immunizing the options trading position from any directional risk. This is due to the fact that deep in the money call options have delta that is close to 1 and that creates a delta neutral position against the stock itself. The position then makes the extrinsic value of the deep in the money call options (which is very little of course) as profit upon expiration. However, this immunity to directional risk is not infinite. The position can still lose money if the stock falls below the strike price of the short call options, which of course would be a very long way down. This results in the following options trading risk graph:
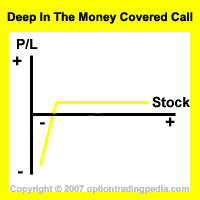
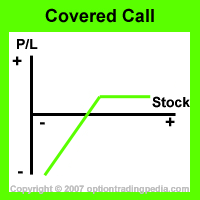
As you can see from above, the maximum profit potential for a regular covered call is way higher than the maximum profit potential of the Deep In The Money Covered Call due to the room given for the stock to appreciate in value as well as the much much higher extrinsic value of the out of the money call options. However, with this increased profitability, the regular Covered Call is subjected to higher options trading risk as the position can start losing money way quicker than the Deep In The Money Covered Call if the stock drops.
As such, the trade-off here is between a higher profit and a higher level of protection. The higher the level of protection (as in a Deep In The Money Covered Call), the lower the profitability. The higher the level of profitability (as in a regular covered call), the lower the level of protection. This is the kind of trade-off that exist in all areas of options trading. There is never a perfect scenario.
Why use Deep In The Money Covered Calls?
Yes, the biggest advantage of Deep In The Money Covered Calls is PROTECTION!
Because Deep In The Money Call Options with delta value of almost 1 are written, these short call options move dollar for dollar against the movement in the stock, thus immunizing it against any directional risk. So how far does this protection go? This protection allows the stock to drop all the way past the strike price of the short call options.
For example, the QQQQ is trading at $29 today and its $22 strike price call options are bidding at $7.30 with a delta value of 0.99, which is almost 1. The $22 strike price all options have an extrinsic value of $0.30, which will be the maximum profit for the position should the stock close at any price above the strike price of the short call options, which is $22. Now, in order for this position to lose money, the QQQQ needs to drop below $22, which is a drop of 24%!
That's how big a protection the Deep In The Money Covered Call grants for making that $0.30 in extrinsic value. It's really as close to an options trading arbitrage as you can get without all the complex options trading calculations. All you have to do is to look for deep in the money call options with enough extrinsic value to worth the trouble. Of course, the profits to be expected would also be like in an arbitrage trade... very little. As we all know in options trading, low risk equals to low profits.
Deep In The Money Covered Call as Income Strategy
The advantage of having a predictable options trading return each month using the Deep In The Money Covered Call is also its biggest drawback.
The Deep In The money Covered Call should be regarded as an income strategy in order to make a predictable monthly return in the form of the small extrinsic value of the deep in the money call options because the position will no longer benefit from any gains in the stock. Yes, for the protection and predictable return, you will give up any speculative profits should the stock should suddenly stage a rally. This is because any gains in the stock would be totally offset by the loss in the call options as these call options would move dollar for dollar with the stock.
When To Use Deep In The Money Covered Call?
One should use a Deep In The Money Covered Call when one wishes to make a small, low risk profit without betting on the direction of the stock.
How To Use Deep In The Money Covered Call?
Establishing a Deep In The Money Covered Call is extremely simple. All you have to do is to write (sell to open) 1 contract of deep in the money call option for every 100 shares you own.
| Deep In The Money Covered Call Example : Assuming you own 700 shares of QQQQ at $29. Sell To Open 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan22Call. |
Which strike price should you choose for the call options to be written?
There are just 2 simple criterias:
1. The delta value of the call options need to be 0.99 to 1. This is to completely neutralize the directional risk of the position.
2. The selected option needs to have enough extrinsic value to return a profit above what you will pay in expenses in the form of brokerage commissions.
Profit Potential of Deep In The Money Covered Call :
The Deep In The Money Covered Call's maximum profit is the extrinsic value of the short call options. This happens as long as the price of the stock remains above the strike price of the call options all the way to expiration of the short call options.
Profit Calculation of Deep In The Money Covered Call:
% Profit = total extrinsic value of call options / total outlay of position
|
Deep In The Money Covered Call Example :
Assuming you own 700 shares of QQQQ at $29. Sell To Open 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan22Call. Assuming the Jan22Calls are bidding at $7.30. % Profit = ($0.30 x 700) / ($29 x 700) = 210 / 20,300 = 1.03% profit. |
Risk / Reward of Deep In The Money Covered Call:
Upside Maximum Profit: Limited
Maximum Loss: Unlimited
Happens when the stock drops below strike price of short call options.
Losing Point of Deep In The Money Covered Call:
The losing point of the Deep In The Money Covered Call is the price below which the position starts to make its loss.
Losing Point = Strike price of short call options - extrinsic value of short call options.
|
Deep In The Money Covered Call Example :
Assuming you own 700 shares of QQQQ at $29. Sell To Open 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan22Call. Assuming the Jan22Calls are bidding at $7.30. Losing Point = $22 - $0.30 = $21.70. |
Advantages Of Deep In The Money Covered Call:
:: Profiting as long as stock remains above strike price of short call options.
:: Very deep stock position protection.
Disadvantages Of Deep In The Money Covered Call:
:: Maximum profit is very small.
Alternate Actions for Deep In The Money Covered Calls Before Expiration :
1. If the price of the stock drops to the strike price of the short call options before expiration and is assessed that the stock could rebound, you could buy to close the short call options, which should now be worth very little, and then buy to open at the money put options to transform the position into a protective put position in order to profit when the stock rebounds and yet be protected should the drop continues.
Deep In The Money Covered Call Questions
:: Deep In The Money Covered Calls Without Owning The Shares?
:: How To Get DITM Covered Call Assigned Early?
:: Combining Covered Call with Straddle?
:: Deep In The Money Covered Call On Indexes?

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by