How Does The Covered Put Work in Options Trading?
Covered Put - Introduction
The Covered Put, also known as Selling Covered Puts, is a lesser known variant of the popular Covered Call option strategy. In a Covered Call, you buy shares
and sell call options against it in order to profit from a stagnant or bullish move while in a Covered Put, you short shares and then sell put options
against it in order to profit from a stagnant or bearish move.
Studying the Covered Call first makes the Covered Put easier to understand.
|
|
The Covered Put is not a common strategy that most option traders use when speculating a
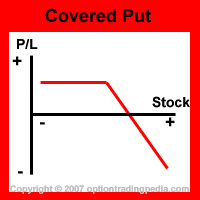
stagnant or bearish move in the underlying stock as a Covered Put has a limited profit potential along with an unlimited loss potential. Couple this
with the fact that most shares rise over time, the Covered Put is always exposed to the danger of unlimited loss. When speculating a quick bearish
move on the underlying stock, most option traders prefer to use other complex bearish strategies which profits from both a bearish and
stagnant move on the underlying move like the Bear Ratio Spread.
A Covered Put is most commonly used by share traders to
increase the profits from shorting shares and also to protect a short share position against a slight rise in price. In the first scenario,
if the underlying stock should drop to the strike price of the put options sold, one would make the drop in price on the underlying stock plus
the premium on the put options sold as profit. In this case, the premium on the put options sold serves as additional profits. In the second
scenario, the premium on the put options serves to offset the loss on the short shares should the underlying stock rise.
When To Use Covered Put?
One should use a Covered Put when one wishes to increase one's profits when shorting shares or to protect one's short share position from a slight rise in price.
How To Use Covered Put?
Establishing a Covered Put is extremely simple. All you have to do is to write (sell to open) 1 contract of nearest out of the money put option for every 100 shares you shorted.
|
Covered Put Example
Assuming you shorted 700 shares of QQQQ at $44. Sell To Open 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan43Put. |
Profit Potential of Covered Put :
The Covered Put's maximum profit occurs when the stock closes exactly at the strike price of the short put options at expiration.
|
Covered Put Example
From the above example : Assuming your 700 QQQQ close at $43 upon expiration of the 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan43Put. You will make the $1 move in QQQQ plus the value of the 7 Jan43Put that you wrote as profit. |
Such an ideal situation is, of course, rare. In most cases, the short put options will either be in the money or out of the money at expiration.
|
Covered Put Example
From the above example : Assuming your 700 short QQQQ close at $43.50 upon expiration of the 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan43Put. You will make $0.50 from the QQQQ move plus the whole value of the 7 Jan43Put. |
When the underlying stock drops below the strike price of the short puts options upon expiration, further gain in value on the short shares will be offset by an equivalent rise in value on the put options that you sold. This means that if the underlying stock drops below the strike price of the short put options, the position will stop rising in value.
|
Covered Put Example
From the above example : Assuming your 700 QQQQ close at $42 upon expiration of the 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan43Put. You will gain $2 from the short shares, $1 from the short put option's premium value and lose $1 on the short Jan43Puts as it goes $1 In The Money for a net gain of $2. |
Profit Calculation of Covered Put:
Maximum profit = (Short Stock Price - Strike Price) + Option Bid
|
Covered Put Calculations
Assuming you bought 700 QQQQ close at $44 and sold 7 contracts of QQQQ Jan43Put @ $1.00. Maximum Profit = ($44 - $43) + $1.00 = $2.00 |
Risk / Reward of Covered Put:
Maximum Profit: Limited
Break Even Point of Covered Put:
Breakeven point for Covered Puts is the point where the position will start losing money if the underlying stock rises instead of fall.
Break Even = Short Stock Price + Option Bid
| Following up from the above example : $44 + $1.00 = $45.00 |
Advantages Of Covered Put:
Disadvantages Of Covered Put:
Adjustments for Covered Puts Before Expiration :
1. If you expect the underlying stock to fall drastically, you should buy to close the short put options.
Questions on Covered Put
:: "Difference Between Selling Put and Covered Put?"

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
| Javascript Tree Menu |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by