How Does Protective Call work in Options Trading?
Protective Call - Introduction
While
Protective Puts are used to protect profits in a
long stock position, Protective Calls are used to protect profits in a short stock position.
Protective Call uses call options to hedge short stock positions while preserving profitability if the stock continues to fall.
Without Protective Call, the only way a stock trader can protect unrealised profits on short stock positions is to liquidate (buy back)
a part of the holding. However, liquidating part of the holding denies the stock trader access to future profits should
the stock continue to fall. Options trading solves this dilemma using Protective Call.
|
|
Protective Call is simple
options trading strategy involving the purchase of
at the money call options
whenever you wish to "lock in" the profits on your short stock position. Once the Protective Call is in place,
the call options will appreciate in step with any appreciation in the stock price, hedging against any losses completely.
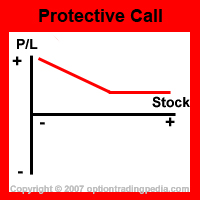
Protective Call creates a position known as a synthetic long put in options trading as it transforms the unlimited profit and loss characteristics of the short stock position into an unlimited profit (albeit restricted to the remaining value of the stock) and limited loss position, just like a put option. You could also create the same profit/loss profile as Protective Call using only a fraction of the money involved in the Protective Call by using another options trading strategy known as the Fiduciary Put.
When To Use Protective Call?
You would use Protective Call whenever your short stock position has appreciated to the point where it's profits must be protected while keeping further profitability open.
|
Protective Call Example :
Assuming you shorted 100 shares of XYZ at $40 on 1 Jan. XYZ falls to $30 within a few days and you wish to hold on for future appreciation without risking a short term pull up. |
How To Use Protective Call?
Protective Call is a simple options trading strategy where you simply buy to open 1 contract of at the money call options for every 100 shares that you shorted.
|
Protective Call Example :
To seal in that $10 appreciate in value, you would buy to open 1 contract (equivalent to 100 shares) of $30 Call Options expiring a few months later (e.g March30Call for $0.80). |
Profit Potential of Protective Call :
Protective Call is an options trading hedging strategy which, combined with the underlying short stock position, grants unlimited maximum profit as long as the underlying stock continues to fall.
Profit Calculation of Protective Call :
The cost of the Call Options are expensed against the rise in value of the short stock position when calculating profits.
|
Protective Call Example :
Assuming XYZ falls to $20 by the expiration of the March30Call. Profit = ($30 - $20 - $0.80) x 100 = $920 |
STOCK PICK MASTER!
"Probably The Most Accurate Stock Picks In The World..."
Risk / Reward of Protective Call:
Upside Maximum Profit: Unlimited (restricted by value of stock remaining)
Maximum Loss: Limited
Break Even Point of Protective Call:
Because you incur a cost on the call options, the underlying stock needs to fall to cover that cost. The breakeven
point is the point beyond which the Protective Call position would continue to profit.
Breakeven = Initial stock price - cost of call options bought.
|
Protective Call Example :
Breakeven = $30 - $0.80 = $29.20 |
Advantages Of Protective Call:
Disadvantages Of Protective Call:
Alternate Actions for Protective Call Before Expiration :
1. If the underlying stock continues to fall strongly, one could sell the
out of the money call options and then buy at the money call
options in order to re-establish the Protective Call position at the lower price.
2. If the underlying stock rallies strongly, one should continue to hold the Protective Call position all the way to expiration.
Alternate Actions for Protective Call During Expiration :
1. During expiration, if the call options are in the money
due to a rise in the underlying stock, you could sell the call options on expiration day.

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
| Javascript Tree Menu |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by