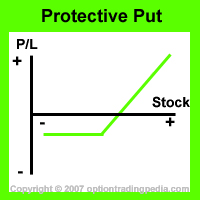
What Is Protective Put Options and how does it insure your stocks from a crash?
Protective Puts - Introduction
Do you wish to buy "insurance" for your stocks to prevent their values from dropping?
Yes, you can with a simple options strategy called "Protective Put"!
Protective Puts is an option trading hedging strategy used to hedge against a drop in stock price. Protective Puts are very similar to Married Puts and is a popular option trading strategy amongst stock traders. Protective Puts protect your stock's unrealised profits, so that you don't have to sell any shares to lock in the profits so far.
Without stock options, the only way a stock trader can protect unrealised profits on shares is to liquidate (sell) a part of the holding. However, liquidating part of the holding denies the stock trader access to future profits should the stock continue to do well. Option trading solves this dilemma using Protective Puts.
|
|
Protective Puts - How It Works
Imagine this, if a stock trader could "buy an insurance" on his shares at it's present price such that if it drops below the present price, the "insurance" would compensate the reduction in the stock price 100%, wouldn't that help all stock traders hold on to their stocks longer and reap more future profits? Wouldn't that help reduce risk dramatically? This is where the Protective Puts option trading strategy come in.
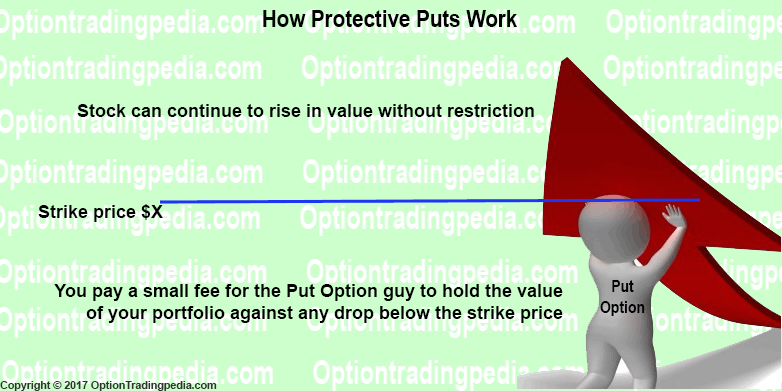
Protective Puts is simply buying at the money put options whenever you wish to "lock in" your share's profits. Once the Protective Put is in place, the put options will appreciate in step with any depreciation in the stock price, hedging against any losses completely.
Protective Put Example :Assuming you own 100 shares of XYZ at $40 and it appreciated to $60. Now, the only way you can guarantee that $60-$40 = $20 profit is by selling your shares, right? Now, if you sell your shares, what if the price of XYZ continues to go higher? Won't you have missed out on the profits? This is when you can simply buy 1 contract of XYZ $60 strike price put options in order to buy "insurance" for your XYZ stock at $60! Assuming XYZ company got hit by an unforeseen scandal and its stock price drops from $60 to $10. Even though you would lose $60 - $10 = $50 x 100 shares = $5000, your put options value would actually rise to $60 - $10 = $50, making you a $50 x 100 = $5000 profit, completely offsetting the $5000 loss on the stocks, thereby insuring you against the loss and protecting the value of your portfolio. |
Protective Puts - What It Cost
Now, put options are not free. Put options comes at a fraction of the price of the stock, known as a "Premium". You pay a premium for insurance even if it is not used, right? That's exactly the same for Protective Puts. You pay the premium on the put options exactly as you would pay an insurance premium. If the price of the underlying stock continues to rise, the put options expires out of the money eventually when its "contract period" is over, incurring the cost of the put options as expense, exactly like an insurance plan.
How much is the "premium" on a put option? For instance, GOOG (Google Inc.) closed at $823.31 (27 Jan 2017) and its January $822.50 put options are trading at about $13.00, which is only 1.58% of the value of the GOOG stock itself. So, just paying 1.58% of the value of the stock buys you complete protection against GOOG dropping below $822.50 for a month! In fact, if you could take a bit of risk, buying the protective put at the $800 strike price only cost about $6, which is only 0.7% of the value of GOOG's stock! A small fee for a huge protection!
|
|
When To Use Protective Puts?
You would use Protective Puts whenever your stocks have risen to the point where it's profits must be protected.
How To Use Protective Puts?
Protective Puts is a simple option trading strategy where you simply buy to open 1 contract of at the money put options for every 100 shares that you own.
What if you own less than 100 shares of the underlying stock?
Good news is, there are now Mini Options on most of the most heavily traded stocks that represent only 10 shares instead of 100 shares. So if you own just 10 shares of the underlying stock, even if its slightly lesser than 10 shares, you could simply buy 1 contract of its Mini put options instead.
What if you owned quite a few different stocks instead?
Well, if you own quite a few different stocks in a single portfolio, you could actually try to hedge the portfolio as a whole by buying put options on the ETF that most closely represent your portfolio, be it QQQ for Nasdaq, DIA for the Dow or SPY for the S&P500.Trading Level Required For Protective Put
A Level 1 options trading account that allows the execution of Covered Call and Protective Put is needed. Read more about Options Account Trading Levels.
Profit Potential of Protective Puts :
Protective Puts is an option trading hedging strategy which, combined with the underlying stock, grants unlimited maximum profit as long as the underlying stock continues to rise.
Profit Calculation of Protective Puts :
The cost of the Put Options are expensed against the rise in price of the underlying stock when calculating profits.
Profit = (stock price - put strike price - cost of put) x number of shares
|
Following up from the above example:
Assuming XYZ rises to $60 by the expiration of the Put options. Assuming the put options cost $1.00 Profit = ($60 - $40 - $1) x 100 = $1900 |
STOCK PICK MASTER!
"Probably The Most Accurate Stock Picks In The World..."
Risk / Reward of Protective Puts:
Upside Maximum Profit: Unlimited
Break Even Point of Protective Puts:
Because you incur a cost on the put options, the underlying stock needs to rise to cover that cost. The breakeven point is the point beyond which the Protective Puts position would start to profit.
Breakeven = Initial stock price + cost of put options bought.
|
Following up from the above example:
Breakeven = $50 + $0.80 = $50.80 |
Advantages Of Protective Puts:
Disadvantages Of Protective Puts:
Alternate Actions for Protective Puts Before Expiration :
1. If the underlying stock continues to rally strongly, one could sell the out of the money put options and then buy at the money put options in order to re-establish the Protective Puts position at the higher price.
2. If the underlying stock drops strongly, one should continue to hold the Protective Puts position all the way to expiration.
Alternate Actions for Protective Puts During Expiration :
1. During expiration, if the put options are in the money due to a drop in the underlying stock, you could sell the put options on expiration day and then use the profits made to buy more of the underlying stock in preparation for a rebound, effectively compounding your profits.
2. During expiration, if the put options are out of the money due to the underlying stock rising, one should simply let the put options expire worthless rather than incurring costs by selling them.
Questions Relating To Protective Puts...
Why Isn't The Protective Puts Bearish?
Protective Put Videos

Protective Put on KO stocks

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by