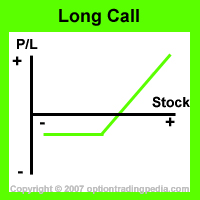
Learn how to buy call options for options trading profits through the long call option strategy.
Long Call Options - Introduction
Buying call options, or also known as Long Call Options or simply Long Call, is the simplest bullish option strategy ever and is a great starting point for beginner option traders.
Buying call options
/ Long Call Options offers the protection of limited downside loss with the benefit of leveraged gains. When applied correctly, it allows even beginner option traders
to consistently make more profits than losses.
|
|
Buying Call Options / Long Call Options is in reality, a leveraged way of trading the underlying stock for much more profits on the same move in the stock. One should be familar with call options before executing this strategy. Please read all about call options here.
When To Buy Call Options / Long Call Options?
Buying Call Options / Long Call Options is an extremely versatile option strategy where one can use when:
1. Confident of a dramatic short term rise in the underlying stock
Because call options depreciate daily due to time decay, one would want
the underlying stock to rise quickly so that one can sell the call option for a profit before it expires.
2. Wants to control more of the underlying stock using lesser money to hold for long term gain
When one is bullish on an underlying stock and wants to control it for a lesser price for the long term, buying call options
LEAPS is an
ideal strategy and a leveraged alternative to holding stocks.
|
Long Call Example
GOOG is trading at $473.23 per share at the time of this writing. Each lot of 100 shares would cost traders $47,323.00, which is not usually an amount beginner traders has. One could instead control the same 100 shares of GOOG and benefit from the same move for 7 months if it goes up through buying call options / long call options on it's call options with another 7 months to expiration for only $4,860.00 per contract, which is only 10.26% of the price of GOOG. That is the discounting effect of Buying Call Options / Long Call Options. This allows you to take a maximum risk of only $4,860 no matter how low GOOG goes in the future rather than risking the whole $47,323 in an outright stock trade. |
How To Buy Call Options / Long Call Options?
There are actually 2 ways to execute a buy call options / Long Call Options strategy... I shall simply refer to them as the Beginner way and the Veteran Way.
The Beginner Way To Buying Call Options / Long Call Options
The beginner way to buying call options / Long Call Options is simply to buy At The Money (ATM) call options
of the stock you think is going to go up. This is known as the "At The Money Long Call".
|
At The Money Long Call Example
Assuming QQQQ at $44. Buy To Open 10 contracts of QQQQ Jan44Call. |
The Veteran Way To Buying Call Options / Long Call Options
Veterans buying call options / Long Call Options need to consider delta values and strike prices when choosing what specific strike price to buy the
call options at in order to fulfill one's investment and portfolio needs.
|
Out Of The Money Long Call Example
Assuming QQQQ at $44. Veteran expects QQQQ to rise quickly to $50. Veteran buys to open 10 contracts of Jan$46Call. |
In this case, QQQQ needs to rise beyond $46 to turn in a profit by expiration. If QQQQ rises but not to beyond $46, the call options
would be worthless by expiration but if QQQQ rises before expiration but not beyond $46, one could still turn in a profit based on the delta
value of the call options. In fact, veteran option traders rarely hold a stock option contract to expiration. This is also the buying call options / Long Call Options
method that will turn the highest profit in percentage but comes also with the highest risk of loss. As such, veteran options traders only use very small capital committments (money they can afford to lose) for such an options strategy as its a little like buying a lottery ticket.
Veteran Option Trader Method 2 : Veterans expecting the underlying stock to rise moderately and wishes to maximise profits
would buy In The Money (ITM) Options as ITM options contains higher
delta value than At The Money Options. This is known as an "In The Money Long Call".
|
In The Money Long Call Example
Assuming QQQQ at $44. Veteran expects QQQQ to rise moderately. Veteran buys to open 10 contracts of Jan$43Call. |
How deep In The Money (ITM) to buy the call options at is really up to the trade management need of the individual but in essence, one would not
go lower than the first strike price that turns in a delta value of 1 or 0.99. This method of buying call options / Long Call Options is less risky as one would still
have some value left over at expiration if the underlying stock stayed stagnant but will also turn in less profit per cent then the Out of the money
(OTM) method above.
| Assume QQQQ Rise To $47 From $44. | |||||||
| Method | Price | Delta | Profit Before Expiration | Profit @ Expiration | Loss If QQQQ Expires @ $44 | Risk Ranking | Profit Ranking |
| Beginner Way | $0.80 | 0.5 | +187.5% | +275% | -100% | 2 | 2 |
| Veteran Method 1 | $0.10 | 0.159 | +477% | +900% | -100% | 1 | 1 |
| Veteran Method 2 | $1.80 | 0.862 | +43.66% | +22.22% | -44.4% | 3 | 3 |
It's clear from the above table that no matter what method of Buying Call Options / Long Call Options you choose to execute, you will always end up with more profit per cent than simply buying QQQQ stocks. A trader who simply bought QQQQ stocks at $44 would only make 6.8% profit when QQQQ rises to $47. The Options Leverage involved in using each of the above methods can also be mathematically measured to help make a more informed decision when buying call options.
Profit Potential of Buying Call Options / Long Call Options :
Buying call options / Long Call Options allows you to profit with unlimited ceiling. That means that your profit grows as long as the underlying stock continues to rise, unlike other more complex strategies like the Bull Call Spread where the position stops making money after the underlying stock reaches a certain level. In this sense, Buying Call Options / Long Call Options is one of the few option strategies that has unlimited profit potential.
Trading Level Required For Buying Call Options
A Level 2 options trading account that allows the buying of call and put options without the owning the underlying stock is needed for buying call options. Read more about Options Account Trading Levels.
Profit Calculation of Buying Call Options / Long Call Options :
There are 2 ways to calculate profit for Long Call Options : Before Expiration and After Expiration.
Before Expiration
One can predict the rise in the value of the call options for every $1 rise in the underlying stock using the delta value of the
call option, and hence it's profit.
|
Following up from the above example:
Buy to open 10 QQQQ Jan44call for $0.80 per contract. QQQQ rises to $47 the next day. Delta value of Jan44Call is 0.5. Profit = [($47 - $44) x 0.5] / 0.8 = 187.5% profit. |
 Please note that the above figures are only arbituary and that precise calculation of expected profit before expiration can only be arrived at
using a stock option pricing model such as the Black Scholes Model.
That is because delta value increases as a call option gets more and more in the money.
Please note that the above figures are only arbituary and that precise calculation of expected profit before expiration can only be arrived at
using a stock option pricing model such as the Black Scholes Model.
That is because delta value increases as a call option gets more and more in the money.
|
After Expiration
Upon expiration, call options will be left with the value of the stock above it's strike price. If that value is greater than
the original premium value of the call options, the position turns a profit. ( Read
About How To Calculate Premium Value Of An Option Here )
|
Following up from the above example:
Buy to open 10 QQQQ Jan44call for $0.80 per contract. QQQQ rises to $47 at expiration. Profit = [(Price of Underlying Stock - Strike Price) - premium value of call options] / Price of Call Options Profit = [($47 - $44) - 0.80] / 0.80 = 275% profit |
Risk / Reward of Buying Call Options / Long Call Options:
Upside Maximum Profit: Unlimited
Maximum Loss: Limited
Net Debit Paid. The most one could lose is the entire amount put forward into buying call options when the underlying stock expires out of the money (OTM).
Break Even Point of Buying Call Options / Long Call Options:
Again, there are 2 ways to determine break even point for buying call options / long call options. Before Expiration and After Expiration.
Before Expiration
Before expiration, the bid/ask spread of the call options is the breakeven point.
|
Following up from the above example:
QQQQ Jan44Call has a bid price of $0.78 and an ask price of $0.80. Because one buy at the ask price and sell at the bid price, the difference of $0.02 becomes the breakeven point beyond which one would start to profit. |
After Expiration
After expiration, the underlying stock needs to move more than the premium value in the call option in order to result in a profit. Thus the breakeven point becomes the entire premium value of the call option.
|
Following up from the above example:
QQQQ Jan44Call is At The Money and has no intrinsic value. The whole price of $0.80 is premium value. Thus the breakeven point would be $44 + $0.80 = $44.80. QQQQ needs to move more than $44.80 by expiration in order to result in a profit. |
Advantages Of Buying Call Options / Long Call Options:
Disadvantages Of Buying Call Options / Long Call Options:
Alternate Actions for Buying Call Options / Long Call Options Before Expiration :
1. If the underlying stock is expected to slow down its advance or halt by a certain price, one could sell to open a corresponding amount of out of the money call options, transforming the position into a Bull Call Spread, in order to reap an additional profit or to hedge against a small pullback in the price of the underlying stock.
2. Alternatively, if one wishes to protect the profits in one's position, one could place a delta neutral hedge.
3. If the underlying stock proves to be very volatile and moves up and down in big swings, then one could buy a corresponding number of put options and transform the position from a long call option into a long strangle where one can profit no matter if the stock expires higher or lower.
Adjustments for Buying Call Options / Long Call Options During Expiration :
1. Exercise the call options. One could exercise the call option if it is In The Money in order to buy the stock at better than market price and hold. An option trader would do this only when one wishes to hold the stock for long term appreciation or dividends.
2. Sell the call options. This is the most popular choice of option traders. Simply sell the call option and realise the profits so far.
3. Roll the position forward. If one continues to be bullish on the underlying stock, one could perform what we call a rolling forward. This is a simple procedure where one sells the expiring call options and buy call options of the following month.
Questions on Buying Call Options
:: Instant Profit Buying ITM Call Options?
:: How Do I Pay For Exercising Profitable Call Options?
:: Repairing Losing Long Call Options?
:: Will My Call Options Remain Till Expiration?
:: Remedy for Losing Call Options Position?
:: How Do I Get Good Stocks To Buy Call Options On?
Videos On Buying Call Options
 Video: AAPL Long Call |
 Video: Closing A Long Call |

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
Probably the most accurate long call options picks ever... 85% Accuracy Achieved in 2021!
| Javascript Tree Menu |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by