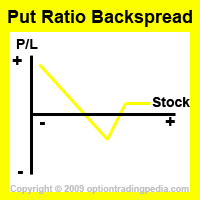
How Does The Put Ratio Backspread Work in Options Trading?
Put Ratio Backspread - Introduction
As you can tell from its name, Put Ratio Backspreads are Ratio Backspreads, which means volatile options strategy. Backspreads profit when the underlying stock breaks out to upside or downside and loses money when the stock remains stagnant. This is what happens with the Put Ratio Backspread but with a slight twist. Put Ratio Backspreads are credit spreads but retained the unlimited profit potential of debit volatile options trading strategies! Yes, credit backspreads such as the Short Butterfly Spread and Short Condor Spread have only limited profit potential, whereas the Put Ratio Backspread has unlimited profit potential when the stock breaks out to downside and limited profit potential when the stock breaks out to upside, opening up one direction for unlimited profit. This tutorial shall cover how Put Ratio Backspreads work, when to use it, how to use it and its advantages and disadvantages.
|
|
More a Bearish Strategy than a Volatile Strategy
The Put Ratio Backspread is a
vertical ratio spread. Even though the Put Ratio Backspread is technically a
volatile options trading strategy due to the fact that it can profit either upwards or downwards, it does has a strong directional bias, which is downwards. Yes, Put Ratio Backspreads can be better understood as a bearish options strategy which still makes a limit amount of money even if the stock goes up strongly. It makes an unlimited profit if the stock goes down and a small profit if the stock goes up. Of course, like all bearish options trading strategies, it loses money if the stock stays still. If understood this way, the Put Ratio Backspread becomes the only credit bearish options strategy to have unlimited profit potential. Indeed, the Put Ratio Backspread does empitomize the versatility and flexbility of ratio spreads, creating unique options trading risk/reward profiles.
If the underlying stock is assessed to have more upside breakout potential than downside, then the Call Ratio Backspread should be used instead in order to open up unlimited profit potential to upside.
When To Use Put Ratio Backspread?
One should use a Put Ratio Backspread when one is confident in a strong drop in the underlying instrument, wishes to profit from that drop without any upfront payment and still make some money should the stock rises instead.
How To Execute Put Ratio Backspread?
The Put Ratio Backspread involves buying more at the money or out of the money Put Options than the number of in the money Put Options are shorted.
|
Example: Assuming QQQQ at $44.
Buy To Open 2 QQQQ Jan44Put @ $1.05, Sell To Open 1 QQQQ Jan47Put @ $3.15 As the 2 Jan44Put costs $1.05 x 2 = $2.10, the 1 Jan47Put actually covers the entire price of the long Put Options and results in a net credit of $1.05. |
The ratio of long and short Put Options depends largely on the preference of the individual trader. A common ratio is the 2 : 1 ratio spread where you sell to open 1 In The Money (ITM) put option for every 2 At The Money (ATM) or Out of the Money (OTM) Put Options that was bought.
What Strike Prices To Use In Put Ratio Backspread?
The main deciding factor when determining what ratio
to establish the Put Ratio Backspread with is strike price. Here are the effects of different strike prices being used :
1. The wider the strike price difference between the short and long Put Options, the lesser In The Money (ITM) Put Options you would need to
sell in order to cover the price of the long Put Options, the bigger the profit if the stock goes up but the further the higher breakeven point becomes.
From the guidelines above, it is obvious that the higher we expect the net credit to be, the higher the stock needs to rise in order to profit to upside. This is the kind of compromise every options traders should be familar with in options trading. As such, we should always choose to sell the nearest in the money (ITM) Put Options which covers the total price of the long Put Options without exceeding the number of long Put Options bought.
Profit Potential of Put Ratio Backspread :
The Put Ratio Backspread has an unlimited profit potential to downside and will keep making more profit as long as the underlying stock keeps dropping. It also has limit profit potential to upside and will make the net credit as profit if the stock rises above the upper breakeven point.
Profit Calculation of Put Ratio Backspread:
Profit = ((long put strike - stock price) x number of Long Put Options) - (((short put strike - stock price) - short put intrinsic value) x number of short put options)
|
Profit Calculation of Put Ratio Backspread:
Assuming QQQQ at $44. Buy To Open 2 QQQQ Jan44Put @ $1.05, Sell To Open 1 QQQQ Jan47Put @ $3.15. Assume QQQQ drops to $41. Because you paid nothing to put on this position, profit % is infinite. You made money out of nothing. |
Maximum loss = Total Premium Value Of Long Put Options - Total Premium Value Of Short put options
|
Profit Calculation of Put Ratio Backspread:
Assuming QQQQ at $44. Buy To Open 2 QQQQ Jan44Put @ $1.05, Sell To Open 1 QQQQ Jan47Put @ $3.15. Maximum Loss = ($1.05 x 200) - (($3.15 - $3) x 100) = $210 - $15 = $195 when QQQQ closes at $44 upon expiration. |
Risk / Reward of Put Ratio Backspread:
Upside Maximum Profit: Unlimited
Maximum loss occurs when the underlying stock closes exactly at the strike price of the Long Put Options.
Break Even Point of Put Ratio Backspread:
There are 2 breakeven points for a Put Ratio Backspread. The Lower Breakeven Point is point below which the position will start
to make a profit. The Upper Breakeven Point is the point above which the position will make in profit the net credit received.
Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price Of the Short put options.
|
Profit Calculation of Put Ratio Backspread:
Continuing from the previous example: Upper Breakeven Point = $47 If the stock rises above $47, the position will make the net credit of $105 as profit upon expiration. |
Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price Of Long Put Options - (Maximum loss / (number of Long Put Options - number of short put options))
|
Profit Calculation of Put Ratio Backspread:
Assuming QQQQ at $44. Buy To Open 2 contracts of QQQQ Jan44Put @ $1.05, Sell To Open 1 contract of QQQQ Jan47Put @ $3.15. Net credit = $105, Maximum Loss = $195 Lower Breakeven Point = 44 - (195 / (200 - 100)) = 44 - 1.95 = $42.05 |
 As you noticed from above, the Put Ratio Backspread offers the best of both worlds as long as the underlying stock moves significantly up or down.
As you noticed from above, the Put Ratio Backspread offers the best of both worlds as long as the underlying stock moves significantly up or down.
|
Advantages Of Put Ratio Backspread :
Disadvantages Of Put Ratio Backspread :
Alternate Actions Before Expiration :
1. If the position is already in profit and the underlying stock is expected to continue it's drop, you could
buy to close the
short Put Options, transforming the position into a Long Put Option
in order to maximise profits.
2. If the position is in profit and the underlying stock is expected to reach a certain price by expiration or stay stagnant at a certain lower price,
one could buy to close the short Put Options and then sell to open Put Options at the strike price which the underlying stock is expected to drop to. This
transforms the position into a Bear Put Spread. Such is the flexibility of trading stock options.

|
Don't Know If This Is The Right Option Strategy For You? Try our Option Strategy Selector! |
| Javascript Tree Menu |
Important Disclaimer : Options involve risk and are not suitable for all investors. Data and information is provided for informational purposes only, and is not intended for trading purposes. Neither www.optiontradingpedia.com, mastersoequity.com nor any of its data or content providers shall be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Data is deemed accurate but is not warranted or guaranteed. optiontradinpedia.com and mastersoequity.com are not a registered broker-dealer and does not endorse or recommend the services of any brokerage company. The brokerage company you select is solely responsible for its services to you. By accessing, viewing, or using this site in any way, you agree to be bound by the above conditions and disclaimers found on this site.
Copyright Warning : All contents and information presented here in www.optiontradingpedia.com are property of www.Optiontradingpedia.com and are not to be copied, redistributed or downloaded in any ways unless in accordance with our quoting policy. We have a comprehensive system to detect plagiarism and will take legal action against any individuals, websites or companies involved. We Take Our Copyright VERY Seriously!
Site Authored by